SNMPv3 Request Tool
Linux offers excellent SNMP support and is generally the preferred operating system for SNMP-based tools and troubleshooting. In environments where Linux is not an option, Windows Server presents a challenge because its native SNMP support is extremely limited. Despite this, many Network Management Systems (NMS) have historically been developed for Windows platforms.
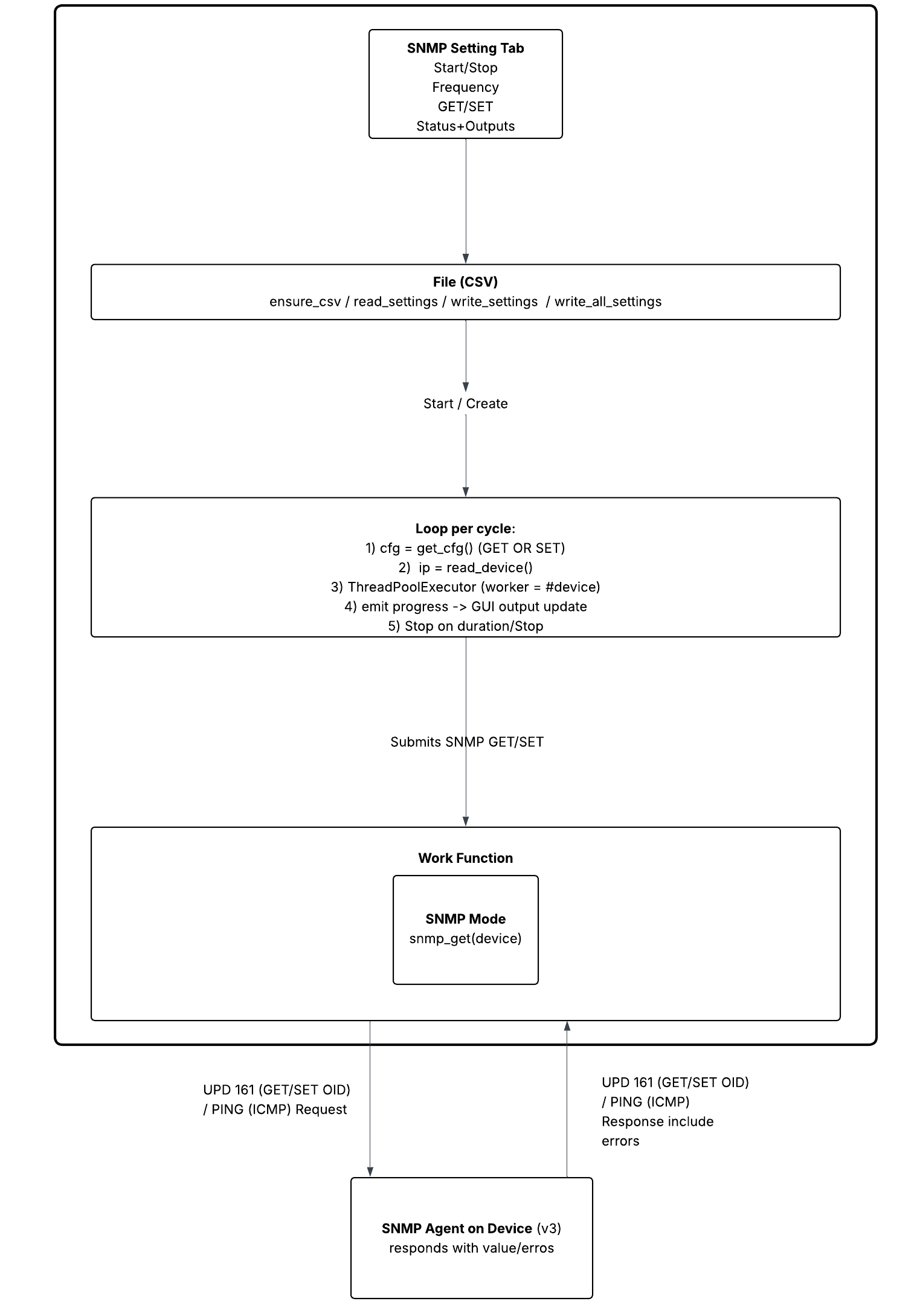
The script below demonstrates the internal workflow of an SNMP GET/SET utility. It can be used in a lab environment to better understand SNMP operations and assist with troubleshooting.
What it does
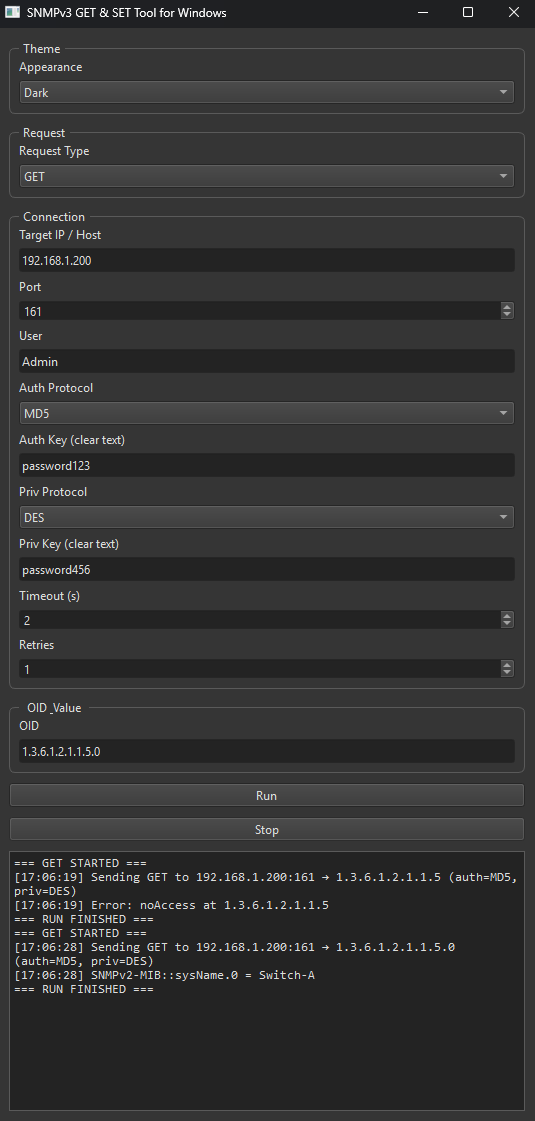
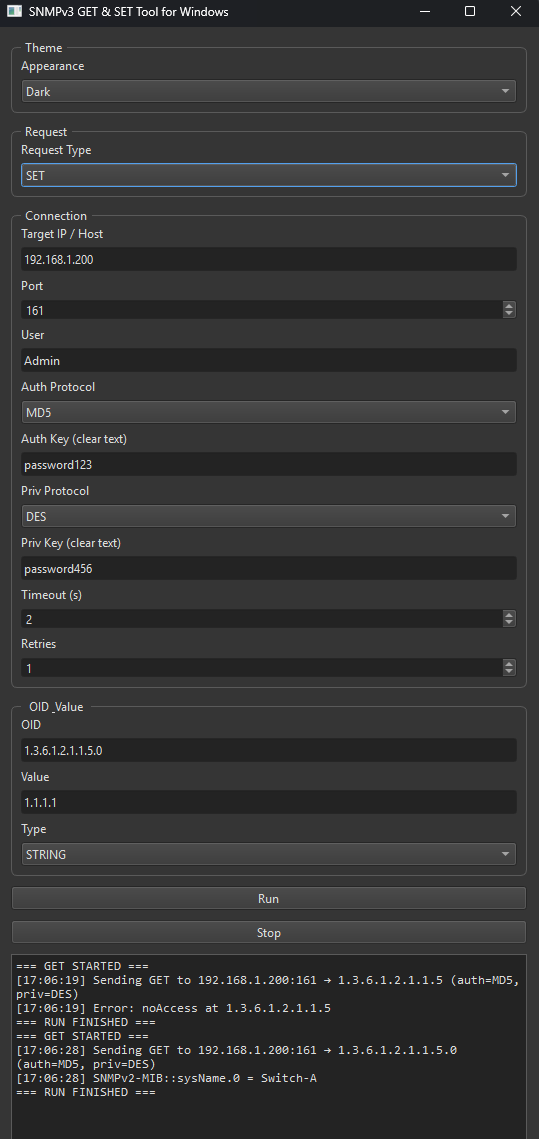
Operations: SNMPv3 GET and SNMPv3 SET via dropdown menu.
UI logic: When GET is selected, the Value and Type inputs are hidden. This is because SNMP GET requests do not attempt to apply a value thus needing to define the type of value. SNMP SET requires a value and type of value which is defined by the equipment. OID’s which have been defined as write only allow for a certain value type to be written to it.
Threaded execution: Runs requests in a background QThread so the UI stays responsive; Stop is best-effort.
Logging: Timestamped lines in a large, read-only output box (errors and results).
Security (SNMPv3 USM)
Auth protocols (HMAC): NONE, MD5, SHA, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384 and SHA512.
Priv (encryption): NONE, DES, 3DES, AES AES128, AES192 and AES256.
Rule enforced: Privacy requires Auth (authPriv only) — choosing a priv protocol with NONE auth is blocked in the UI/worker.
Connection & retries
Target/Port: User-entered host/IP and UDP port (default 161).
Timeout/Retries: Parameters can be defined in the application
User credentials: Username, Auth key, Priv key (shown in clear text, by design).
Data entry & types
OID: Entered as a string; used via ObjectIdentity(oid).
SET value types supported:
INTEGER, UNSIGNED32, GAUGE32, COUNTER32, COUNTER64 and TIMETICKS
.OCTETSTRING or STRING.
OID (Dotted OID).
IPADDRESS (IPv4 dotted).
Value coercion: Numbers cast with int(), hex parsed for OctetString (odd nibble padded), others via constructor.
What the script outputs
GET: Each varbind as OID = value.
SET: Echoes SET OK: OID = value on success.
Errors: Prints SNMP engine errors and PDU errors.
UX behavior
Form layout: All fields vertical (label above control).
Validation: Basic checks for target/user/OID; extra checks for SET (value type).
Single job guard: Prevents starting a new request while one is running.
Not included (by design / current code)
SNMPv1/v2c (community strings) — Whilst it would be easy to include these two versions it is not recommended to use them as they offer no encryption over the network so can be freely read when capturing network traffic.
GET-NEXT / GET-BULK, table walks — Perhaps something to consider implementing in the future but for now no plans.
Multiple OIDs in one request — single OID per run. As this is just a test project it was not implemented however further improvements could allow for multi OID’s to be set either in the same SNMP packet or individually in separate SNMP packets.
Trap/Inform receiver or sender — Trap and Inform is not in the scope of this project but further reading on this can be found in the in articles on this site.
MIB loading/translation — Not included as development would be too heavy for a small project like this. Many SNMP MIB browsers and NMS allow for third party mibs to be imported.
IPv6 address type — IpAddress in pysnmp module only supports IPv4. I would consider IPv4 to be more widely used in network equipment at this with addresses being statically set with IPv6 perhaps more considered for IOT.
SNMP Get Request Tool Window
SNMP Set Request Tool Window
SNMP Get/Set - Sequence Diagram